Hiperurisemia adalah penyebab gout dan urolithiasis akibat pembentukan dan deposisi kristal monosodium urat. Hiperurisemia sering dijumpai pada penyakit ginjal kronis karena terjadi penurunan clearance asam urat. Penelitian menunjukkan bahwa asam urat berperan dalam progresi penyakit kardiovaskular dan penyakit ginjal kronis. Peningkatan asam urat serum berperan penting terhadap resistensi insulin dan hipertensi, yang berkontribusi pada munculnya sindrom metabolik kardiorenal. Tingkat asam urat yang tinggi dapat berkontribusi pada cedera ginjal akibat disfungsi endotel dengan gangguan pembentukan nitric oxide, aktivasi sistem renin-angiotensin-aldosteron, peningkatan stres oksidatif oleh NAPDH oksidase, dan sistem imun maladaptif yang dapat meningkatkan fibrosis pada jaringan vaskular, jantung, dan ginjal serta abnormalitas fungsi yang terkait.
Allopurinol adalah obat yang digunakan secara konvensional untuk menurunkan sintesis asam urat dengan mekanisme kerjanya yaitu xanthine oxidase inhibitor. Dengan menghambat xanthine oxidase, allopurinol diketahui berperan sebagai efek anti-inflamasi pada atherosklerosis, gagal jantun kongestif, dan cedera gijal akut. Penelitian juga membuktikan bahwa cedera ginjal yang disebabkan oleh peningkatan tingkat asam urat dapat dicegah dengan menggunakan allopurinol.
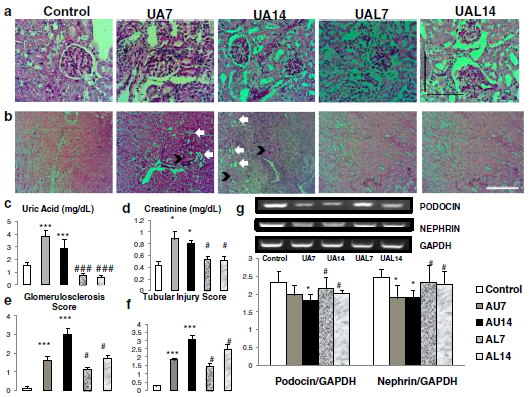
Penelitian kami menunjukkan bahwa kondisi hiperurisemia dapat menyebabkan cedera ginjal dengan peningkatan skor glomerulosklerosis dan cedera tubulus dengan penurunan penanda podosit (podocin dan nephrin). Perbaikan cedera ginjal dapat dilihat pada kelompok allopurinol. Hiperurisemia pada mencit dipicu dengan injeksi asam urat 125 mg/kgBB secara intraperitoneal. Injeksi NaCl dilakukan pada grup mencit kontrol (control). Mencit diterminasi pada hari ke-7 (UA7) dan hari ke-14 (UA14). Kelompok allopurinol (UA7 dan UA14) dilakukan dengan suplementasi allopurinol 50 mg/kgBB per oral.
Asam urat menginduksi adanya glomerulosklerosis dan cedera tubulus serta penurunan penanda pada podosit. (a-b) Gambar representatif dari glomeruloskerosis dengan pengecatan PAS. (b) Gambar representatif cedera tubulus dengan pengecatan PAS. Cedera tubulus ditandai dengan dilatasi tubulus (panah putih) dan intraluminal cast (panah hitam). Injeksi asam urat dapat menginduksi glomerulosklerosis dan cedera tubulus pada mencit. (c) Tingkat asam urat serum lebih tinggi pada grup UA7 dan UA14. (d-f) Tingkat kreatinin, skor glomerulosklerosis dan cedera tubulus lebih tinggi pada grup UA. (g) Penurunan ekspresi mRNA nephrin dan podocin dengan RT-PCR menunjukkan kerusakan podosit pada grup UA.
Referensi:
Haryono A, Nugrahaningsih DA, Sari DC, Romi MM, Arfian N. Reduction of Serum Uric Acid Associated with Attenuation of Renal Injury, Inflammation and Macrophages M1/M2 Ratio in Hyperuricemic Mice Model. Kobe Journal of Medical Sciences. 2018;64(3):E107.
Romi, M.M., Arfian, N., Tranggono, U., Setyaningsih, W.A.W. and Sari, D.C.R., 2017. Uric acid causes kidney injury through inducing fibroblast expansion, Endothelin-1 expression, and inflammation. BMC nephrology, 18(1), p.326.
Filiopoulos V, Hadjiyannakos D, Vlassopoulos D. New insights into uric acid effects on the progression and prognosis of chronic kidney disease. Ren Fail. 2012;34:510–20.
Gustafsson D, Unwin R. The pathophysiology of hyperuricaemia and its possible relationship to cardiovascular disease, morbidity and mortality. BMC Nephrol. 2013;14(1):1.
Chaudhary K, Malhotra K, Sowers J, Aroor A. Uric acid-key ingredient in the recipe for cardiorenal metabolic syndrome. CardioRenal Med. 2013;3(3):208–20.
Iliesiu A, Campeanu A, Dusceac D. Serum uric acid and cardiovascular disease. Mædica. 2010;5(3):186–92.
Zoccali C, Maio R, Mallamaci F, Sesti G, Perticone F. Uric acid and endothelial dysfunction in essential hypertension. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17(5):1466–71.
Papežíková I, Pekarová M, Kolářová H, Klinke A, Lau D, Baldus S, et al. Uric acid modulates vascular endothelial function through the down regulation of nitric oxide production. Free Radic Res. 2013;47(2):82–8.
Choi YJ, Yoon Y, Lee KY, Hien TT, Kang KW, Kim KC, et al. Uric acid induces endothelial dysfunction by vascular insulin resistance associated with the impairment of nitric oxide synthesis. FASEB J. 2014;28(7):3197–204.
Kanbay M, Yilmaz MI, Sonmez A, Turgut F, Saglam M, Cakir E, et al. Serum uric acid level and endothelial dysfunction in patients with nondiabetic chronic kidney disease. Am J Nephrol. 2011;33(4):298–304.
Mazzali M, Hughes J, Kim YG, Jefferson JA, Kang DH, Gordon KL, et al. Elevated uric acid increases blood pressure in the rat by a novel crystal-independent mechanism. Hypertension. 2001;38(5):1101–6.
Sánchez-Lozada LG, Soto V, Tapia E, Avila-Casado C, Sautin YY, Nakagawa T, et al. Role of oxidative stress in the renal abnormalities induced by experimental hyperuricemia. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008;295(4):F1134–41.
Baldwin W, Mcrae S, Marek G, Wymer D, Pannu V, Baylis C, et al. Hyperuricemia as a mediator of the proinflammatory endocrine imbalance in the adipose tissue in a murine model of the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes. 2011;60(4):1258–69.
Pacher P, Nivorozhkin A, Szabo C. Therapeutic effects of xanthine oxidase inhibitors: Renaissance half a century after the discovery of allopurinol. Hum Physiol. 2006;58(1):87–114.
Kim IY, Lee DW, Lee SB, Kwak IS. The role of uric acid in kidney fibrosis: Experimental evidences for the causal relationship. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014(638732):1–9.